Has Tokyo reached ‘peak city’?




Tokyo is often described as crowded, mushrooming, figuratively bursting at the seams. Except, in many ways, it’s not.
Unlike many megacities, the world’s largest metropolitan area has largely stopped growing, either in land or population. Where Mumbai, Lagos or São Paulo continually sprout new informal neighbourhoods that are constantly outstripping the ability of the city to catch up, Tokyo’s urban planning and services more or less seamlessly encompass the central wards and the neighbouring cities of Kawasaki, Yokohama, Chiba and Saitama that form its unbroken metropolitan area.
Despite Japan’s ageing population, Tokyo’s demographics are actually quite middle of the road. Far from being crammed with people, Tokyo is in fact averagely dense – more crowded than some cities, less so than others.
Unemployment and crime are low. Traffic is comparatively well-managed, while the modal share of transit and cycling are high: Tokyo in particular has solved what many cities call the “last-mile” transit problem, by relying on an informal network of cheap bicycles. Gentrification , though a factor, feels less disruptive than in similarly prosperous cities such as London and New York, where entire neighbourhoods are being rewritten at great speed, or most Chinese cities, which are unrecognisable to themselves 15 years ago.
Of course, Tokyo has many problems. Its real estate remains expensive, its sprawl makes for long commute times, it has less green space per capita than one might hope for, and worrying social problems remain. Nor has Tokyo stopped changing: because real estate value is tied so closely to land rather than property, new buildings rarely last longer than 30 years , leading to a constant shedding of the city’s skin.
But is there an argument to be made that Tokyo, having now finished its postwar growth spurt, has reached a kind of maturity? Is this the most stable form of megacity that can exist at present – occupying an equilibrium where the population is stable, change is manageable, and the city’s residents and industries are in some sort of balance?
The city that stopped growing?
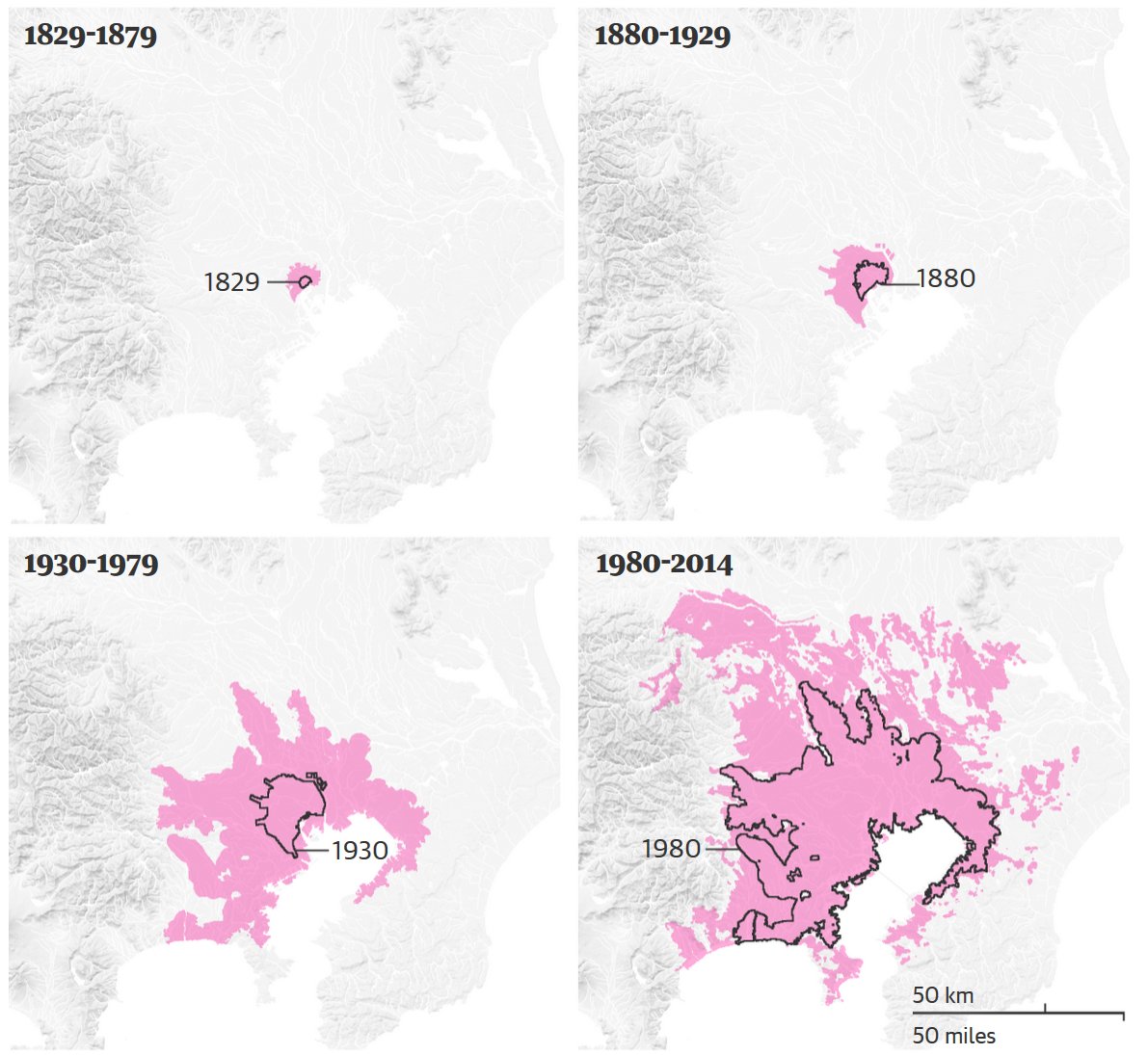
While the cities of Kinshasa and Delhi continue to grow apace , and the Chinese government has actively restricted the growth of Shanghai and Beijing , Tokyo’s population has evened out – in part because it has more or less run out of new land to cover, and in part because of the ageing population of Japan .
“Tokyo is the first megacity to see the end of growth,” says Andre Sorensen, chair of the department of human geography at the University of Toronto, whose 2002 book The Making of Urban Japan was widely praised as key to understanding Japanese urban planning. “It offers important lessons for cities around the world, as ‘peak urban’ will increasingly be seen elsewhere over the rest of this century as the world becomes fully urban and population growth slows and then starts to decline.”
He points out that Japan is essentially “fully urban” – 94.7% of its population lived in cities in 2015 – but thinks Tokyo may now start to contract. “Although the Tokyo core area is currently gaining population because of migration from the rest of Japan and recentralisation from its own suburbs, the region as a whole has already started to lose population. It is projected that the total population of Japan will decrease from 128 million in 2010 to about 87 million in 2060, or by about 800,000 per year.”
How Tokyo became the world’s largest megalopolis, home to about 37 million people
Lincoln Institute of Land Policy, and UN Habitat
“The bell curve of the population age will be 50-60, and the city will contract and become more concentrated,” agrees Mark Dytham of Klein Dytham Architects. “The bulk will slowly evaporate leaving a stronger essence of the city and I think in the next 20 years in 2040 you are going to see the city stop contracting as birth rate levels out.”
Although immigration is increasing, it remains a relative drop in the bucket.
“Tokyo is clearly at or near its peak population, at the high point of the rollercoaster ride, the point when the distant horizon comes into view, just before the nose points down, gravity takes charge, and downward acceleration begins,” Sorensen says. “Although few demographers are willing to say so, it is hard to imagine the factors sufficient to end this decline.”

There are several megalopolises that are not headed for disaster... but not necessarily for paradise, either.
Which ones do you appreciate... or execrate?